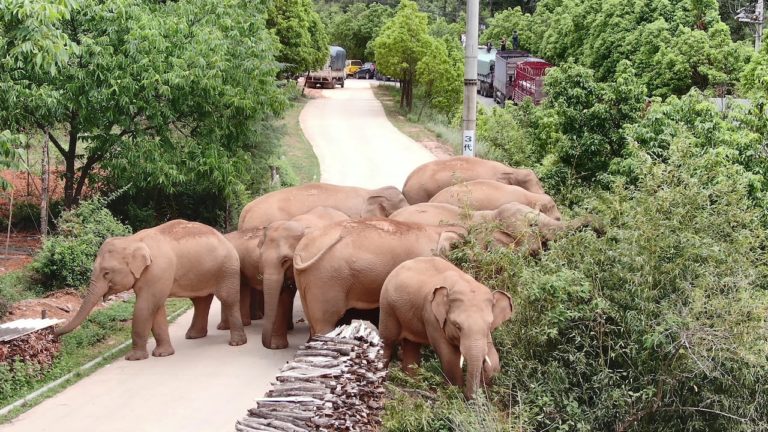
A herd of wandering elephants in Yunnan province has captured the world’s attention. Although humorous and adorable, their odd migratory patterns caused a lot of problems.
Yunnan’s forest fire brigade had to track these elephants 24-hours a day via both ground and air. Hundreds of personnel and vehicles took part in steering the elephants away from humans.
The two tonnes of food used to lure these elephants was apparently not enough. They also pilfered through over a million dollars worth of crops! The elephants’ trek cost a lot of time and resources.
Why are these elephants behaving so oddly? There is an obvious answer: deforestation.
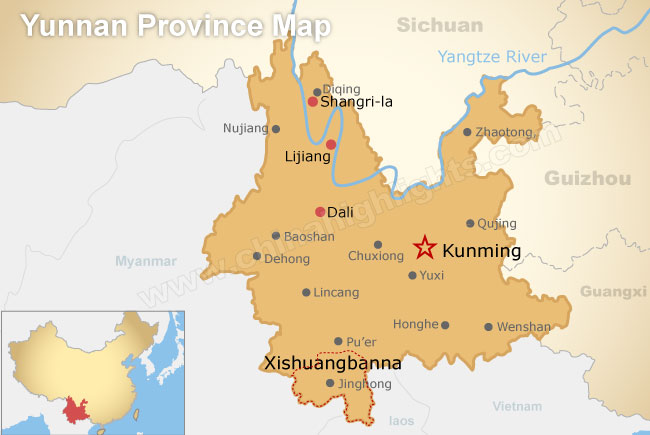 A map of Yunnan. Elephants are found predominantly in Xishuangbanna
A map of Yunnan. Elephants are found predominantly in Xishuangbanna
Source: China Highlights
Some Background
There are two types of elephants: African and Asian. China has a total of about 300 Asian elephants. All these elephants are only found in Yunnan, which borders Myanmar and Laos. Elephant herds seasonally migrate for water, food and mates.
Asian elephants are an endangered species. In an effort to remove the endangered status, the Chinese government has taken steps to conserve elephant habitat.
Their efforts resulted in a slight increase in population, but there were roadblocks along the way.
Due to deforestation for rubber tree plantations and farmland, elephant-human conflicts have increased. (To put into perspective how extensive the rubber industry is in Yunnan: Yunnan’s rubber acreage was 43% of China’s total acreage!)
Now elephants have to venture out of their limited territory to find food, even if that means getting in contact with humans.
Elephants feed on subsistence and cash crops such as corn and sugarcane, which results in losses for farmers. They even break into houses to steal food and salt. From 2011 to 2015, 20 people were attacked in China, resulting in 10 injured and 10 dead.
Elephant-human conflict is a serious issue that plagues many Asian countries like India, Sri Lanka and Vietnam.
 The elephants in Yunnan are of the Indian elephant subspecies. Indian elephants are only found in mainland Asia.
The elephants in Yunnan are of the Indian elephant subspecies. Indian elephants are only found in mainland Asia.
Animal Spot
Possible Solutions
The simplest solution would be to replant trees, but that solution hasn’t worked out as intended. Nature reserves planted towering trees that outcompeted the shrubs and grasses elephants eat.
One county in Yunnan even proposed a controversial plan that involves luring the elephants to a specially constructed area in desperation.
While a specific and effective plan is still in the works, humans need to realize their part in the conflict and attempt to resolve it. Scientists, conservationists and the rubber industry should work together to research solutions.
For example, they can work together to research and replant ecologically beneficial flora in the reserve.
The herd of elephants is still on their trek. It is unclear where their target destination is or when they will return to the elephant reserve.
As of this writing, the elephants are heading toward Kunming, the capital of Yunnan, which is a densely populated city. Hopefully wildlife experts are able to lure them to turn back. We will have to wait and see what these elephants decide to do.
If you want to help with elephant conservation, consider making a donation to WWF, the International Elephant Foundation, Save the Elephants or the Sheldrick Wildlife Trust. You can even adopt a Pygmy Elephant!



0 Comments